
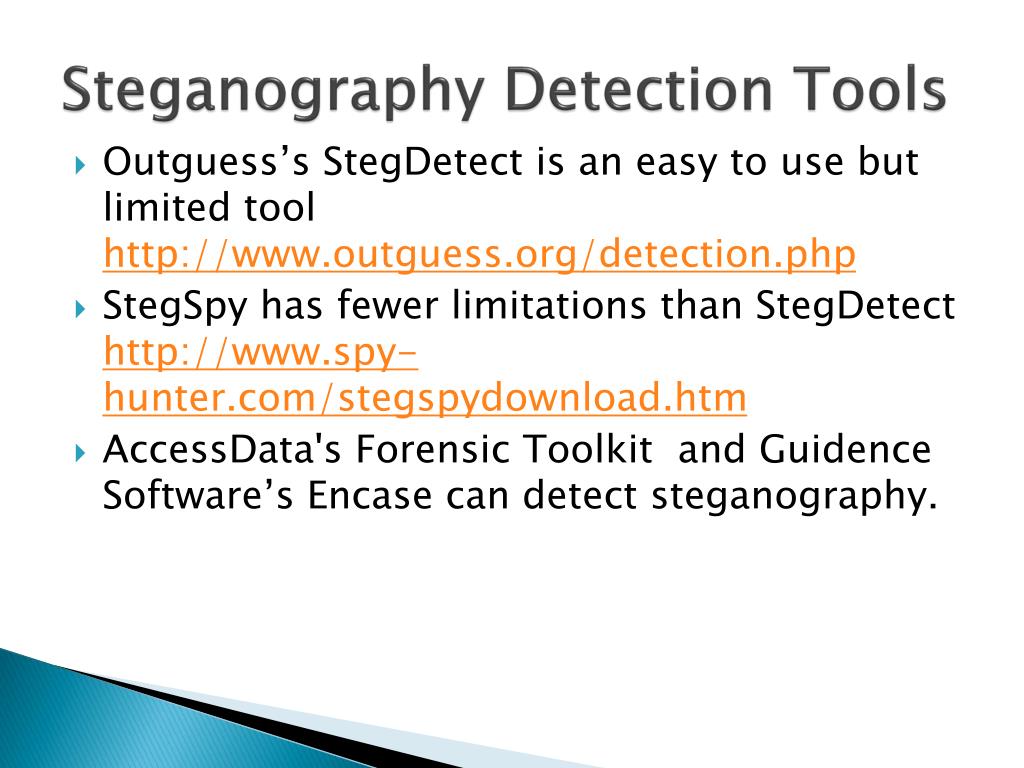
This method can be applied to any steganalysis tool, which gives the analyst a better understanding of the detection results, especially when he has no prior information about the false positive rate of the tool. Additionally, we have provided a detailed statistical analysis for the obtained results to study the difference in detection between selected groups, close groups and different groups of images. This should support the forensic expert to have better interpretation in their results, and taking the false positive rates into consideration. The results obtained show that the rate of false positives generated by Stegdetect depends highly on the chosen sensitivity value, and it is generally quite high. The aim of this study is to help digital forensic analysts, aiming to study a large number of image files during an investigation, to better understand the capabilities and the limitations of steganalysis tools like Stegdetect. In doing so, we process more than 40,000 images randomly downloaded from the Internet using Google images, together with 25,000 images from the ASIRRA (Animal Species Image Recognition for Restricting Access) public corpus. In this paper we analyse Stegdetect, one of the well-known image steganalysis tools, to study its false positive rate. School of Computing, University of Portsmouth, Lion Terrace, Portsmouth PO1 3HE, UK School of Computing, University of Kent, UKĪrticle history: Received 3 October 2012 Received in revised form 8 January 2013 Accepted 24 January 2013 Contents lists available at SciVerse ScienceDirectĭigital Investigation journal homepage: A study on the false positive rate of Stegdetect Omed S.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
